Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example, given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.
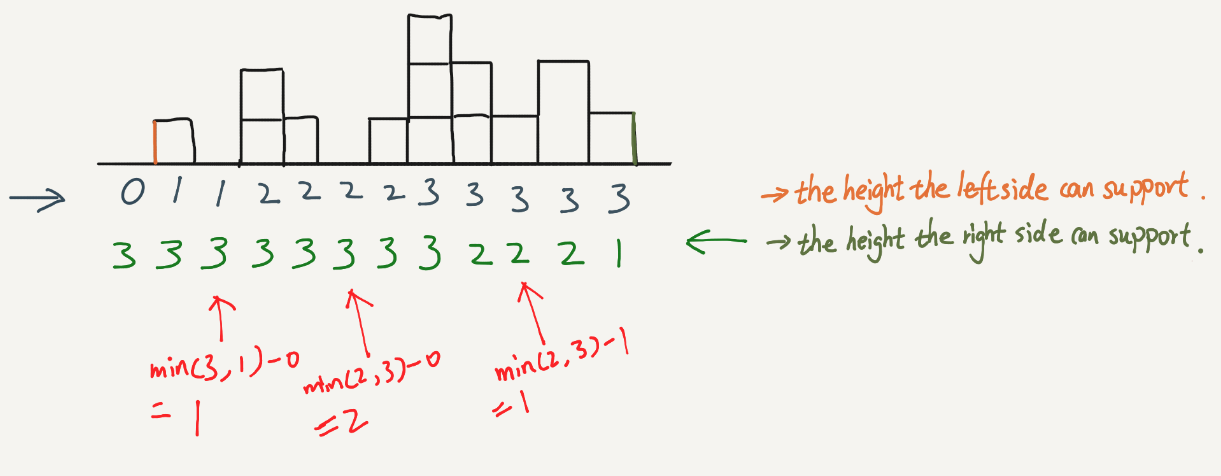
Analysis
This problem is similar to Candy. It can be solve by scanning from both sides and then get the total.
Java Solution
public int trap(int[] height) { int result = 0; if(height==null || height.length<=2) return result; int left[] = new int[height.length]; int right[]= new int[height.length]; //scan from left to right int max = height[0]; left[0] = height[0]; for(int i=1; i<height.length; i++){ if(height[i]<max){ left[i]=max; }else{ left[i]=height[i]; max = height[i]; } } //scan from right to left max = height[height.length-1]; right[height.length-1]=height[height.length-1]; for(int i=height.length-2; i>=0; i--){ if(height[i]<max){ right[i]=max; }else{ right[i]=height[i]; max = height[i]; } } //calculate totoal for(int i=0; i<height.length; i++){ result+= Math.min(left[i],right[i])-height[i]; } return result; } |
I found that solution is very popular and helpful : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WOO27cP8rN4
Check out this solution: https://qr.ae/pGGvzZ
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector& height) {
// maxLeft[i] = max height to the left of i
// maxRight[i] = max height to the right of i
vector maxLeft(height.size()), maxRight(height.size());
if(height.size() == 0) return 0;
maxLeft[0] = height[0];
maxRight[height.size() - 1] = height[height.size() - 1];
for(int i = 1, j = height.size() - 2; i = 0; i++, j--) {
maxLeft[i] = max(maxLeft[i - 1], height[i]);
maxRight[j] = max(maxRight[j + 1], height[j]);
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < height.size(); i++) {
int minFromTwoSides = min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]);
ans += max(minFromTwoSides - height[i], 0);
}
return ans;
}
};
My solution in Javascript (the relevant part):
function calcLeftSideSupport(inputArray){
let resultArray = [];
let tempMax = 0;
for(let i=0; i= tempMax){
tempMax = inputArray[i];
}
resultArray[i] = tempMax;
}
return resultArray;
}
function calcRightSideSupport(inputArray){
let resultArray = [];
let tempMax = 0;
for(let i=inputArray.length-1; i>=0;i--){
if (inputArray[i] >= tempMax){
tempMax = inputArray[i];
}
resultArray[i] = tempMax;
}
return resultArray;
};
function calcRainCapacity(originalArray, leftArray, rightArray){
let rainCapacity = 0;
let rainArray = [];
for(let i=0;i<originalArray.length;i++){
rainArray[i]= Math.min(leftArray[i],rightArray[i]) - originalArray[i];
rainCapacity += rainArray[i];
}
return [rainCapacity,rainArray];
}
function calcMaxHeight(numberArray){
let tempArray = numberArray.slice();
let maxHeight = tempArray.sort(function(a, b){return b-a})[0];
return maxHeight;
}
You can use given heights array to calculate it, firstly see my c++ solution above by using one array instead of two arrays, then you can reuse heights by start from two ends.
int Water::trapping(const vector& heights) {
if (heights.size() < 2) {
return 0;
}
vector heights;
heights.push_back(heights[0]);
for (int i = 1; i = 0; i--) {
int m = i == heights.size() - 1 ? heights[i] : max(heights[i], heights[i + 1]);
heights[i] = min(heights[i], m);
}
int t = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < heights.size(); i++) {
t += min(heights[i], heights[i - 1]);
}
return t;
}
This is a pretty cool solution. Thanks for sharing.
public class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if(height == null || height.length==0) return 0;
int leftMax = 0, rightMax = 0, left = 0, max = 0;
int right = height.length-1;
while(left height[left] ? leftMax : height[left];
rightMax = rightMax > height[right] ? rightMax : height[right];
max += leftMax < rightMax ? leftMax - height[left++] : rightMax - height[right--];
}
return max;
}
}
public class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int l = height.length;
if(l < 3) return 0;
int[] leftMax = new int[l];
int[] rightMax = new int[l];
int maxL = height[0];
int maxR = height[l-1];
for(int i = 0; i maxL ? height[i] : maxL;
leftMax[i] = maxL;
maxR = height[l-1-i] > maxR ? height[l-1-i] : maxR;
rightMax[l-1-i] = maxR;
}
int waterTrapped = 0;
for(int i = 0; i rightMax[i] ? rightMax[i] - height[i] : leftMax[i] - height[i];
}
return waterTrapped;
}
}
Constant O(1) space and O(n) time.
public class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length < 3)
return 0;
int result = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int maxLeft = 0;
int maxRight = 0;
int curHeight;
while (left < right) {
curHeight = Math.min(maxLeft, maxRight);
if (maxLeft < maxRight) {
result += Math.max(curHeight - height[left], 0);
maxLeft = Math.max(height[left], maxLeft);
left++;
}
else {
result += Math.max(curHeight - height[right], 0);
maxRight = Math.max(height[right], maxRight);
right--;
}
}
curHeight = Math.min(maxLeft, maxRight);
result += Math.max(curHeight - height[right], 0);
return result;
}
}
sorry….my mistake….I meant constant space….
Is it possible to do it in constant time? it’s a FB interview question. Haven’t figured out how to do it…