Assume you have an array of length n initialized with all 0’s and are given k update operations.
Each operation is represented as a triplet: [startIndex, endIndex, inc] which increments each element of subarray A[startIndex … endIndex] (startIndex and endIndex inclusive) with inc.
Return the modified array after all k operations were executed.
For example,
Input: length = 5, updates = [[1,3,2],[2,4,3],[0,2,-2]]
Output: [-2,0,3,5,3]
Java Solution 1 – heap
public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) { int result[] = new int[length]; if(updates==null || updates.length==0) return result; //sort updates by starting index Arrays.sort(updates, new Comparator<int[]>(){ public int compare(int[] a, int [] b){ return a[0]-b[0]; } }); ArrayList<int[]> list = new ArrayList<int[]>(); //create a heap sorted by ending index PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new Comparator<Integer>(){ public int compare(Integer a, Integer b){ return updates[a][1]-updates[b][1]; } }); int sum=0; int j=0; for(int i=0; i<length; i++){ //substract value from sum when ending index is reached while(!queue.isEmpty() && updates[queue.peek()][1] < i){ int top = queue.poll(); sum -= updates[top][2]; } //add value to sum when starting index is reached while(j<updates.length && updates[j][0] <= i){ sum = sum+updates[j][2]; queue.offer(j); j++; } result[i]=sum; } return result; } |
Time complexity is O(nlog(n)).
Java Solution 2
We can track each range’s start and end when iterating over the ranges. And in the final result array, adjust the values on the change points. The following shows an example:
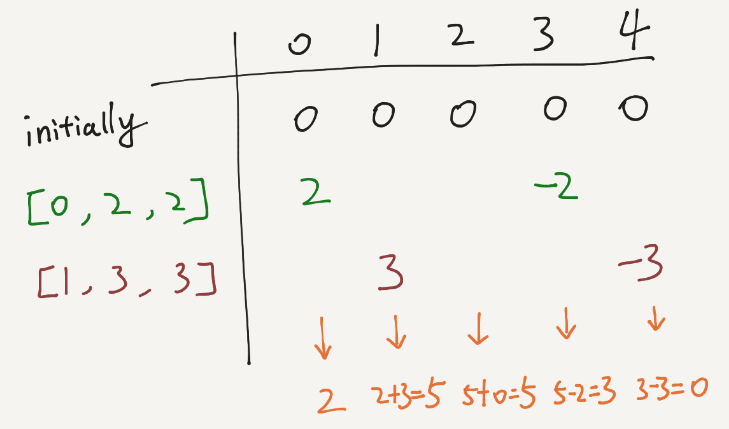
public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) { int[] result = new int[length]; if(updates==null||updates.length==0) return result; for(int i=0; i<updates.length; i++){ result[updates[i][0]] += updates[i][2]; if(updates[i][1]<length-1){ result[updates[i][1]+1] -=updates[i][2]; } } int v=0; for(int i=0; i<length; i++){ v += result[i]; result[i]=v; } return result; } |
Time complexity is O(n).
Whats the second parameter updates , is it updates[startindex][endindex] = inc
why do we need heap here, can someone post the question with example ?
The second solution is super, very smart!