There following Java code shows how to implement a queue without using any extra data structures in Java. We can implement a queue by using an array.
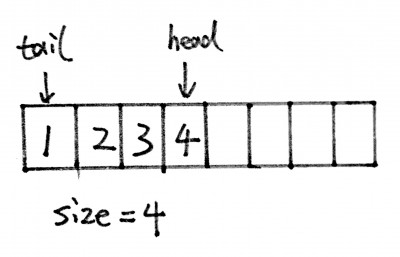
import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.util.Arrays; public class Queue<E> { E[] arr; int head = -1; int tail = -1; int size; public Queue(Class<E> c, int size) { E[] newInstance = (E[]) Array.newInstance(c, size); this.arr = newInstance; this.size = 0; } boolean push(E e) { if (size == arr.length) return false; head = (head + 1) % arr.length; arr[head] = e; size++; if(tail == -1){ tail = head; } return true; } boolean pop() { if (size == 0) { return false; } E result = arr[tail]; arr[tail] = null; size--; tail = (tail+1)%arr.length; if (size == 0) { head = -1; tail = -1; } return true; } E peek(){ if(size==0) return null; return arr[tail]; } public int size() { return this.size; } public String toString() { return Arrays.toString(this.arr); } public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<Integer> q = new Queue<Integer>(Integer.class, 5); q.push(1); q.push(2); q.push(3); q.push(4); q.push(5); q.pop(); q.push(6); System.out.println(q); } } |
this is a stack, not a queue