Visitor pattern is a design pattern commonly used in the parser of a compiler, such as Eclipse JDT AST Parser.
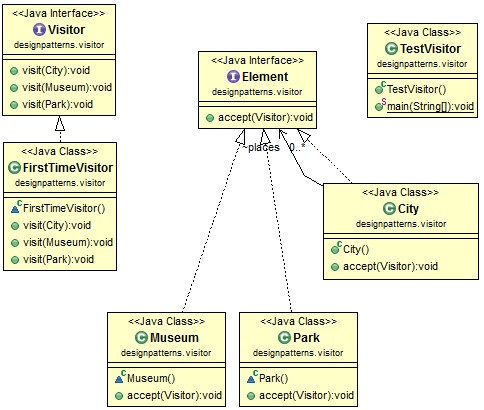
Basically, there are two interfaces – Visitor and Element – in Visitor pattern.
Visitor pattern story
Suppose a first time visitor comes to New York City. He want to visit the city and the city accepts his visit. Once the visitor starts visit, it automatically visit everything, and he doesn’t need to call a method when he wants to go to a museum. The travel is a package!
Visitor pattern class diagram
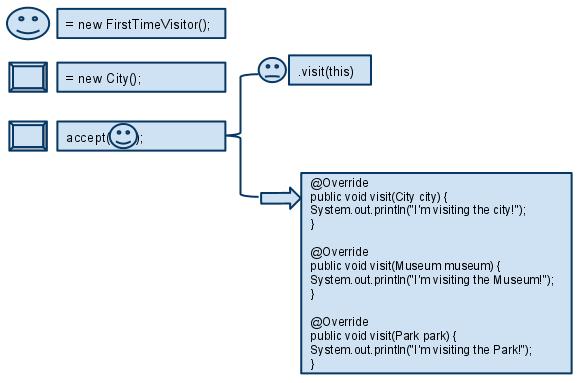
Steps of Visitor pattern
This diagram shows the steps of visiting.
The working process is like the following:
1. A visitor FirstTimeVisitor and an element City are created.
2. Program starts with “City accept a visitor”.
3. The accept method in City defines that let this visitor to visit.
4. Accepted visitor call it’s overloaded method “visit” to visit this City.
Visitor pattern Java code
import java.util.ArrayList; interface Visitor { public void visit(City city); public void visit(Museum museum); public void visit(Park park); } class FirstTimeVisitor implements Visitor { @Override public void visit(City city) { System.out.println("I'm visiting the city!"); } @Override public void visit(Museum museum) { System.out.println("I'm visiting the Museum!"); } @Override public void visit(Park park) { System.out.println("I'm visiting the Park!"); } } interface Element { public void accept(Visitor visitor); } class City implements Element { ArrayList<Element> places = new ArrayList<Element>(); public City() { places.add(new Museum()); places.add(new Park()); } @Override public void accept(Visitor visitor) { System.out.println("City is accepting visitor."); visitor.visit(this); for (Element e : places) { e.accept(visitor); } } } class Museum implements Element { @Override public void accept(Visitor visitor) { System.out.println("Museum is accepting visitor."); visitor.visit(this); } } class Park implements Element { @Override public void accept(Visitor visitor) { System.out.println("Park is accepting visitor."); visitor.visit(this); } } public class TestVisitor { public static void main(String[] args) { FirstTimeVisitor visitor = new FirstTimeVisitor(); City city = new City(); city.accept(visitor); } } |
Output:
I’m visiting the city!
Museum is accepting visitor.
I’m visiting the Museum!
Park is accepting visitor.
I’m visiting the Park!
Visitor pattern in JDK
Hi there,
Very useful post about visitor design pattern.
Thanks for sharing this.
Keep up the good work!
~*~ Software Design and Architecture ~*~
Visitor Design Pattern
-Intent
-Participants
-Structure
-Sequence
-Advantages/Disadvantages
-Example
Visit:
http://www.classworks.info/index.php/bs/bsse/riphah/340-semester6/sda/lectures/683-visitor-design-pattern
Very useful, thank you very much.
I’m trying to integrate this pattern with Java cup to build an Abstract Syntax Tree, But it has been very difficult for me.
Nice simple example…….thanks…!!!