The main idea of Chain of Responsibility design pattern is to build a chain of processing unit, each unit handle the request if threshold is satisfied. Since a chain is built, if one unit is not satisfied, it’s next unit will be tested, and so on. Each request will be process along the chain.
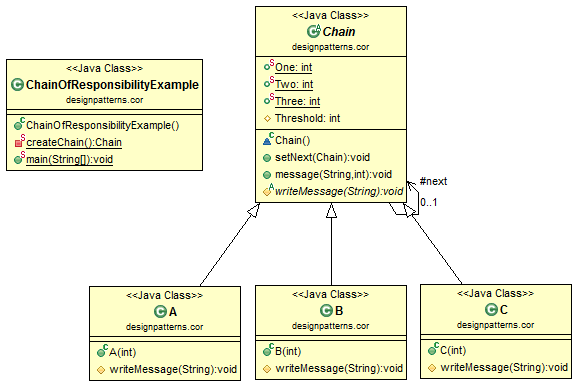
Chain of Responsibility Class Diagram
Chain of Responsibility Java Code
package designpatterns.cor; abstract class Chain { public static int One = 1; public static int Two = 2; public static int Three = 3; protected int Threshold; protected Chain next; public void setNext(Chain chain) { next = chain; } public void message(String msg, int priority) { //if the priority is less than Threshold it is handled if (priority <= Threshold) { writeMessage(msg); } if (next != null) { next.message(msg, priority); } } abstract protected void writeMessage(String msg); } class A extends Chain { public A(int threshold) { this.Threshold = threshold; } protected void writeMessage(String msg) { System.out.println("A: " + msg); } } class B extends Chain { public B(int threshold) { this.Threshold = threshold; } protected void writeMessage(String msg) { System.out.println("B: " + msg); } } class C extends Chain { public C(int threshold) { this.Threshold = threshold; } protected void writeMessage(String msg) { System.out.println("C: " + msg); } } public class ChainOfResponsibilityExample { private static Chain createChain() { // Build the chain of responsibility Chain chain1 = new A(Chain.Three); Chain chain2 = new B(Chain.Two); chain1.setNext(chain2); Chain chain3 = new C(Chain.One); chain2.setNext(chain3); return chain1; } public static void main(String[] args) { Chain chain = createChain(); chain.message("level 3", Chain.Three); chain.message("level 2", Chain.Two); chain.message("level 1", Chain.One); } } |
In this example, level 1 goes through all units in the chain.
A: level 3
A: level 2
B: level 2
A: level 1
B: level 1
C: level 1
A: level 2
B: level 2
A: level 1
B: level 1
C: level 1
This example is simplified from Wiki – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chain-of-responsibility_pattern
Chain of Responsibility Pattern Used in Java JDK
chain-of-responsibility-design-pattern http://k-mingle.blogspot.in/2014/12/chain-of-responsibility-design-pattern.html
I’d refactor Chain class to ChainLink, as it seems logical to have a chain made from links, not from chains.