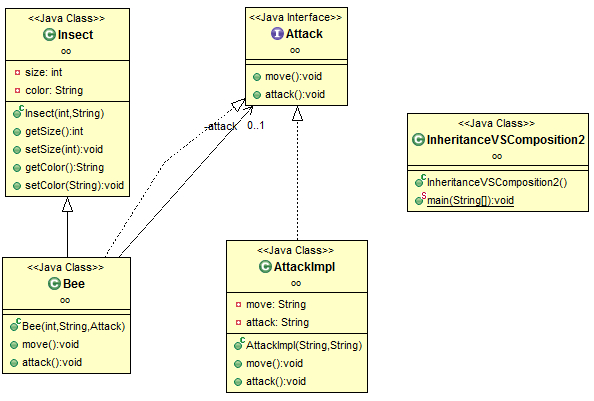
This article illustrates the concepts of inheritance vs. composition in Java. It first shows an example of inheritance, and then shows how to improve the inheritance design by using composition. How to choose between them is summarized at the end.
Versus
Set vs. Set<?>
You may know that an unbounded wildcard Set<?> can hold elements of any type, and a raw type Set can also hold elements of any type. What is the difference between them?
String is passed by “reference” in Java
This is a classic question of Java. Many similar questions have been asked on stackoverflow, and there are a lot of incorrect/incomplete answers. The question is simple if you don’t think too much. But it could be very confusing, if you give more thought to it.
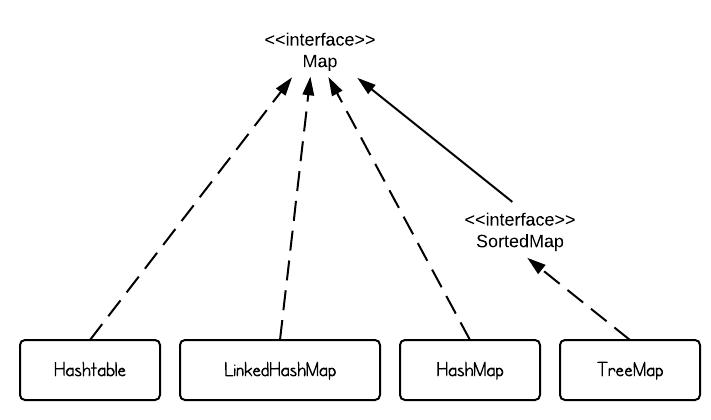
HashMap vs. TreeMap vs. Hashtable vs. LinkedHashMap
Map is one of the most important data structures in Java. In this post, I will illustrate how to use different types of maps, such as HashMap, TreeMap, HashTable and LinkedHashMap. 1. Map Overview There are 4 commonly used implementations of Map in Java SE – HashMap, TreeMap, Hashtable and LinkedHashMap. If we use only … Read more
ArrayList vs. LinkedList vs. Vector
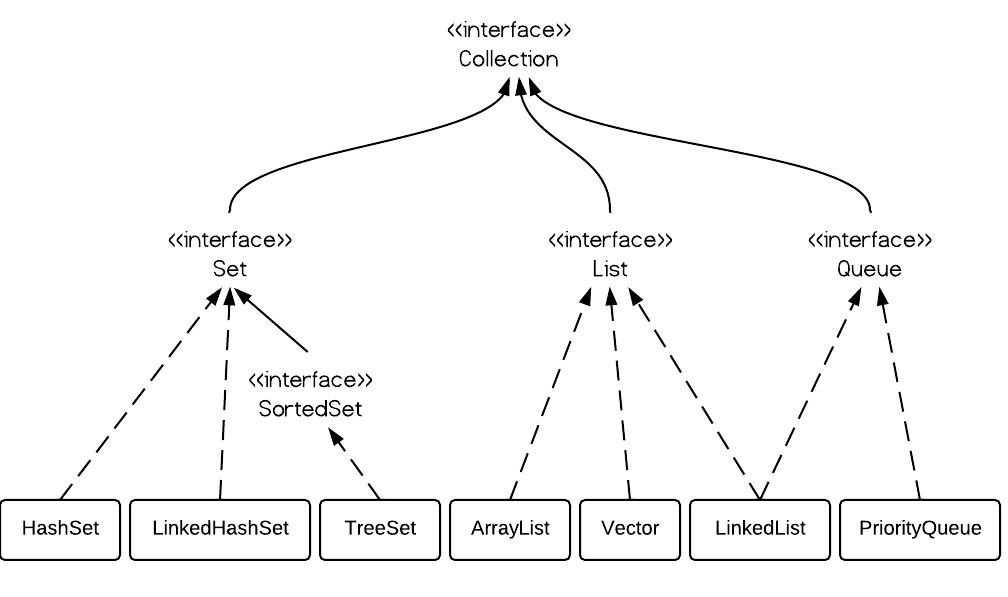
1. List Overview List, as its name indicates, is an ordered sequence of elements. When we talk about List, it is a good idea to compare it with Set which is a set of unique and unordered elements. The following is the class hierarchy diagram of Collection. From the hierarchy diagram you can get a … Read more
HashSet vs. TreeSet vs. LinkedHashSet
A Set contains no duplicate elements. That is one of the major reasons to use a set. There are 3 commonly used implementations of Set: HashSet, TreeSet and LinkedHashSet. When and which to use is an important question. In brief, if you need a fast set, you should use HashSet; if you need a sorted … Read more
10 minutes Perl tutorial for Java developer
This 10 minutes tutorial is not meant to compare Java with Perl. The purpose is to explore how to quickly learn Perl as a Java developer. The following are some key notes from my perspective. 1. Basics to Start Unlike Java, there is no need to claim a “main” method as entry point. To run … Read more
Java vs. Python (2): Data Types
If you know Java and want to quickly get a sense of how to use Python from the very beginning, the following summary can provide you a quick review of data types. You may also find the previous comparison of Java and Python useful. By comparing data types between Java and Python, you can get … Read more
Java vs. Python (1): Simple Code Examples
Some developers have claimed that Python is more productive than Java. It is dangerous to make such a claim, because it may take several days to prove that thoroughly. From a high level view, Java is statically typed, which means all variable names have to be explicitly declared. In contrast, Python is dynamically typed, which … Read more
Static Storage vs Heap vs Stack
The following is the summary of compiler storage allocation. 1. Static vs Dynamic Static: Storage can be made by compiler looking only at the text of the program. One reason for statically allocating as many data objects as possible is that the addresses of these objects can be compiled into target code. Dynamic: Storage can … Read more
Comparable vs. Comparator in Java
Comparable and Comparator are two interfaces provided by Java Core API. From their names, we can tell they may be used for comparing stuff in some way. But what exactly are they and what is the difference between them? The following are two examples for answering this question. The simple examples compare two HDTV’s size. … Read more
Syntactic vs. Semantic vs. Runtime Errors
The following are three Java examples for showing what are syntax error, semantic error, and runtime error. Syntactic Error If a program contains syntax error, it will not pass compilation. public static int returnNull(){ System.out.println("haha"); }public static int returnNull(){ System.out.println("haha"); } Semantic Error If a program contains only semantic errors, it means that it can … Read more
Lucene vs. Database Search
Full-text search mechanism
Lucene’s API interface design is relatively generic, which looks like the structure of the database: tables -> record -> field. Many traditional applications, files, and databases can be easily mapped to the storage structure of Lucene / interface. Overall you can see Lucene as a database system to support full-text index.
FileOutputStream vs. FileWriter
When we use Java to write something to a file, we can do it in the following two ways. One uses FileOutputStream, the other uses FileWriter. Using FileOutputStream: File fout = new File(file_location_string); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fout); BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(fos)); out.write("something");File fout = new File(file_location_string); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fout); BufferedWriter … Read more
An example of C++ dot vs. arrow usage
vs. Overall, dot(.) is for object itself, arrow(->) is for pointer. A good example worth a thousand words. The following example should be a good one. #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Car { public: int number; void Create() { cout << "Car created, number is: " << number << "\n" ; … Read more